Understanding the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) in the EU
The Digital Operational Resilience Act, commonly called DORA, is a significant regulatory framework introduced by the European Union to enhance the financial sector's operational resilience, particularly in the digital age. This act addresses the growing importance of ensuring networks and information security and the operational resilience of financial entities in the EU.
What is the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA)?
Overview of DORA
DORA aims to establish a comprehensive approach to the financial sector's operational resilience within the European Union. It encompasses a wide range of requirements to ensure the security and resilience of the EU financial system, particularly in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
Objective of DORA
The primary objective of DORA is to strengthen the operational resilience of financial entities operating within the EU. It seeks to mitigate the risks associated with ICT-related incidents and enhance the overall security and resilience of the financial sector.
Critical Requirements of Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA)
- Governance and Risk Management
Entities must implement stringent governance structures and risk management processes to identify, manage, and mitigate ICT risks effectively. - ICT Incident Reporting
Mandatory incident reporting mechanisms are established, requiring entities to report significant ICT-related incidents to regulatory authorities promptly. - Digital Operational Resilience Testing
Regular testing of digital systems, including network and information systems, is mandated to ensure resilience to cyber threats and operational disruptions. - Third-Party Risk Management
DORA emphasizes the management of ICT third-party risk, including cloud services and other critical service providers, ensuring they meet the same resilience standards. - Information and Intelligence Sharing
Promotion of information and intelligence sharing about cyber threats and vulnerabilities within the financial industry to enhance collective defense strategies.
Importance of Operational Resilience for the Financial Sector
Operational resilience is crucial for the financial sector, especially in the digital age, as it directly impacts the stability and security of financial services. DORA emphasizes the significance of maintaining operational resilience to safeguard the EU financial system.
Key objectives to strengthen digital operational resilience
Here are vital objectives organizations should focus on to enhance their digital resilience:

- Robust Cybersecurity Measures: Implement comprehensive cybersecurity frameworks that protect against external and internal threats. This includes deploying firewalls, antivirus software, intrusion detection systems, and regular security assessments to identify and mitigate vulnerabilities.
- Effective Incident Response Plan: Develop and regularly update an incident response plan that outlines procedures for responding to cybersecurity incidents and data breaches. This plan should include roles, responsibilities, communication protocols, and recovery steps.
- Regular Data Backup and Recovery Procedures: Establish routine data backup procedures to ensure critical data can be restored during loss or corruption. Test recovery procedures to ensure they are practical and can be executed quickly to minimize downtime.
- Employee Training and Awareness: Foster a culture of security awareness among employees through regular training on cybersecurity best practices, phishing awareness, and the importance of following security protocols. Employees should be equipped to recognize and respond to security threats.
- Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery Planning: Develop comprehensive business continuity (BCP) and disaster recovery plans (DRP) that ensure critical business functions can continue during and after a disruptive event. These plans should be regularly tested and updated to reflect changing business needs and threats.
- Third-Party Risk Management: Assess and manage the risks associated with third-party vendors and service providers. This includes conducting regular audits, ensuring third parties comply with your organization's security standards, and establishing clear contracts that outline responsibilities in the event of a security breach.
- Investment in Advanced Technologies: Leverage advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and blockchain to enhance security, automate threat detection, and improve the efficiency of resilience measures.
- Compliance with Regulations and Standards: Ensure compliance with relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards related to digital security and data protection. Depending on your organization's location and industry, this includes GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, etc.
- Continuous Monitoring and Assessment: Implement real-time monitoring tools to detect anomalies, potential threats, and vulnerabilities. Regularly assess the effectiveness of digital resilience measures and adjust strategies based on emerging threats and technological advancements.
- Culture of Resilience: Cultivate a culture of resilience within the organization that prioritizes adaptability, continuous learning, and proactive risk management. Encourage open communication and collaboration across departments to identify resilience gaps and opportunities for improvement.
Importance of Digital Operational Resilience Testing
Digital operational resilience testing under the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) is crucial for financial entities to:
- Identify Vulnerabilities: Uncover weaknesses that cyber threats could exploit
- Ensure Business Continuity: Maintain operations during ICT disruptions
- Build Stakeholder Confidence: Enhance trust in managing ICT risks effectively
- Support Regulatory Compliance: Meet DORA requirements to avoid penalties
Compliance with Resilience Testing Requirements
Under DORA, resilience testing involves:
- Risk-Based Testing: Proportionate to entity size and complexity
- Scenario-Based Testing: Simulate adverse scenarios for system resilience
- Third-Party Participation: Involvement of critical service providers
- Regular Testing: Frequency aligned with the risk profile
- Reporting and Documentation: Report findings to authorities and take corrective action
| Financial entities strengthen digital operational resilience by implementing these components, ensuring preparedness for ICT disruptions, and safeguarding operations and the financial system. |
How Does DORA Address ICT Third-Party Service Providers?
Regulation of ICT Third-Party Service Providers
DORA establishes regulations about ICT third-party service providers to ensure compliance with the operational resilience requirements. It seeks to mitigate the risks posed by third-party service providers and enhance the overall resilience of the financial sector.
ICT Third-Party Risk Management
DORA emphasizes the identification of critical ICT third-party service providers and imposes specific requirements to enhance their operational resilience. It aims to mitigate the risks associated with essential third-party service providers and strengthen the financial sector's resilience.
How does DORA impact ICT third-party service providers?
The Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) ensures that all financial system participants have safeguards to mitigate cyber threats and ICT-related disruptions. Its impact on financial entities and ICT third-party service providers is significant, aiming to enhance the overall resilience of the financial sector. Below, we explore the requirements of ICT third-party service providers and the management of risks associated with third-party services.
Role of ICT third-party service providers in ensuring operational resilience
ICT third-party service providers are crucial in supporting financial entities to achieve and maintain operational resilience. Their responsibilities include:
- Compliance with DORA Requirements: Adhering to the security standards and practices mandated by DORA, ensuring their services do not become a source of vulnerability for financial entities.
- Transparent Reporting and Communication: Providing timely and transparent communication to financial entities regarding any incidents or potential risks that could impact the entity's operational resilience.
- Supporting Incident Response and Recovery: Collaborating with financial entities in the event of an incident to support rapid response and recovery actions, minimizing the impact on financial services.
- Continuous Improvement of Security Measures: Regularly update and improve security measures to tackle emerging cyber threats, ensuring financial entities' reliance on their services does not expose them to undue risk.
Managing risks associated with third-party services
To effectively manage risks associated with third-party ICT services, financial entities and their service providers must:
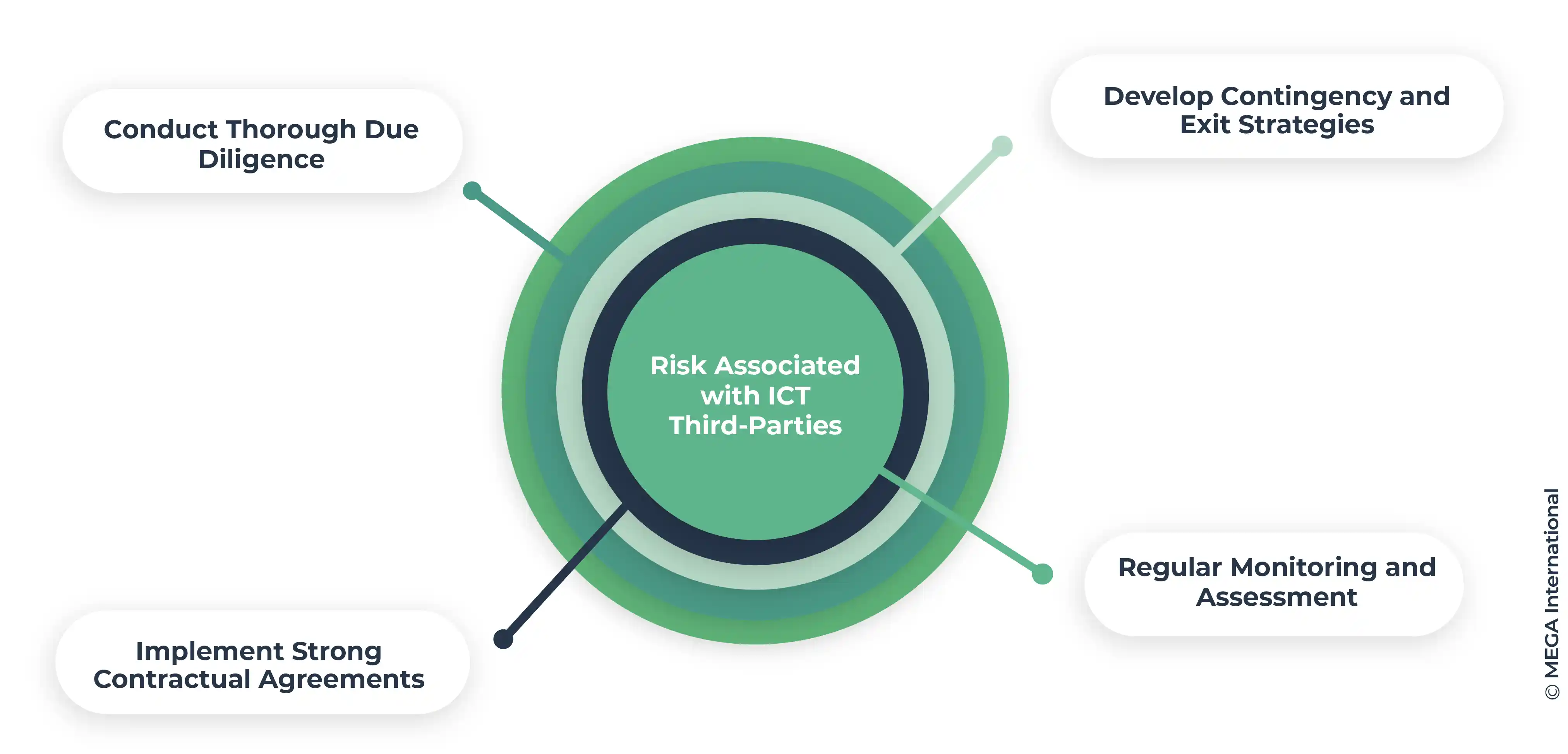
- Conduct Thorough Due Diligence: Evaluate third-party providers' security and resilience practices before engaging their services, ensuring they meet the high standards required by DORA.
- Implement Strong Contractual Agreements: Include specific security standards, incident reporting, and data protection provisions in contracts with third-party providers.
- Regular Monitoring and Assessment: Continuously monitor the performance and compliance of third-party providers, reassessing their risk profile as necessary.
- Develop Contingency and Exit Strategies: Prepare for the possibility of service disruption or termination, ensuring that such events do not critically impact operational resilience.
DORA significantly impacts financial entities and their ICT third-party service providers by establishing a robust regulatory framework focused on digital operational resilience. Through compliance with DORA's requirements, financial entities and third-party providers can contribute to a more resilient and secure financial ecosystem, better prepared to face the challenges of the digital age.
Role of European Securities and Markets Authority in Oversight
The European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) plays a pivotal role in overseeing the implementation of the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA), particularly for entities within the financial market. ESMA's responsibilities in this context include:
- Guidance and Standards Development: ESMA develops guidelines, technical standards, and recommendations to ensure a harmonized approach to implementing DORA across EU member states. This includes clarifying requirements and expectations for financial entities under DORA.
- Monitoring Compliance: ESMA monitors the compliance of financial entities with DORA requirements, working closely with national competent authorities (NCAs) to ensure that the operational resilience framework is effectively implemented across the EU.
- Coordination with Other Authorities: The authority coordinates with other European Supervisory Authorities (ESAs), such as the European Banking Authority (EBA) and the European Insurance and Occupational Pensions Authority (EIOPA), to ensure a consistent application of DORA across different sectors of the financial industry.
- Third-Party Risk Oversight: Given the importance of ICT third-party service providers under DORA, ESMA also oversees the risk management processes that financial entities must have in place regarding their third-party dependencies.
- Incident Reporting Framework: ESMA establishes and maintains the reporting framework, ensuring that significant cyber incidents are reported promptly and consistently.
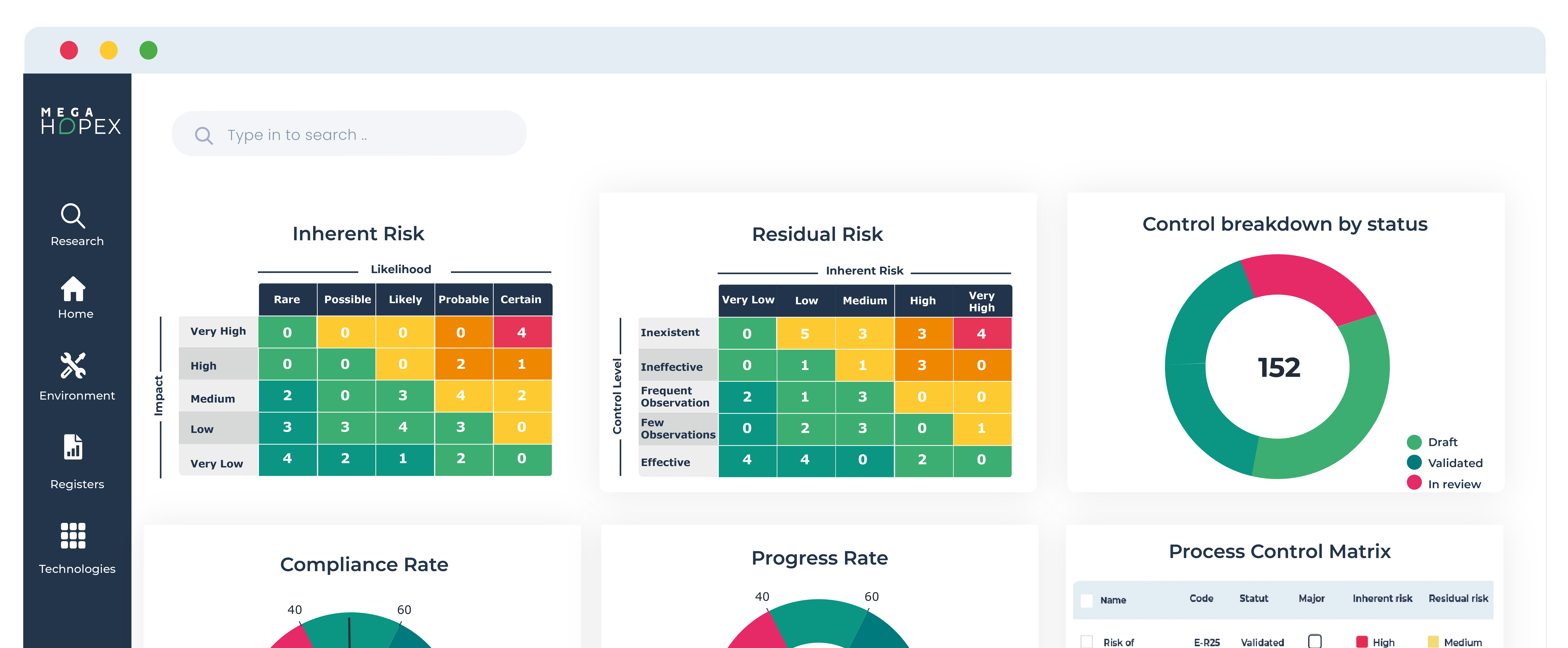
HOPEX and DORA
In the context of the Digital Operational Resilience Act, HOPEX can support financial entities in complying with the regulations' requirements. Here's how HOPEX can assist with DORA:
1. ICT Risk Management Framework
- Risk Identification and Assessment: HOPEX helps identify and assess ICT risks by providing tools to map the organization's digital landscape, including assets, processes, and third-party services. This enables financial entities to pinpoint vulnerabilities and assess their potential impact.
- Risk Mitigation Planning: The platform facilitates the development and implementation of risk mitigation plans. By leveraging HOPEX, organizations can prioritize risks based on their severity and impact and outline appropriate control measures to mitigate them.
2. Incident Management and Reporting
- Incident Tracking and Management: HOPEX offers capabilities for incident management, allowing organizations to record, track, and manage cybersecurity incidents efficiently. This is crucial for meeting DORA's requirements for incident response and recovery.
- Automated Reporting: The platform can automate the generation and submission of incident reports to regulatory authorities, ensuring that reports are timely, accurate, and comply with DORA's reporting guidelines.
3. Operational Resilience Testing
- Continuity planning: HOPEX allows organizations to identify critical operations, build and test their continuity strategy, and monitor operational resilience.
- Testing and Scenario Analysis: HOPEX supports resilience testing by enabling organizations to simulate various cyber threat scenarios and assess the effectiveness of their response strategies. This helps identify gaps in the organization's resilience and make necessary adjustments.
- Documentation and Evidence Management: The platform assists in documenting the testing processes, findings, and corrective actions taken. This documentation is vital for demonstrating compliance with DORA's testing and audit requirements.
4. Third-Party Risk Management
- Vendor Risk Assessment: HOPEX can streamline the process of assessing and managing risks associated with third-party ICT service providers. It provides tools to evaluate vendor compliance with security standards and monitor ongoing risks.
- Automated Reporting: The platform can automate the generation and submission of incident reports to regulatory authorities, ensuring that reports are timely, accurate, and comply with DORA's reporting guidelines.
5. Compliance Management and Reporting
- Regulatory Compliance Dashboard: HOPEX includes features for tracking regulatory compliance, offering dashboards and reporting tools that give an overview of the organization's compliance status with DORA and other relevant regulations.
- Gap Analysis and Remediation Tracking: The platform can facilitate gap analysis to identify areas where the organization falls short of DORA's requirements and track the progress of remediation efforts to address these gaps.
| By leveraging HOPEX, financial entities can enhance their digital operational resilience, streamline compliance with DORA, and effectively manage the complex landscape of risks in the digital age. HOPEX platform's integrated approach to GRC helps organizations comply with regulatory requirements and strengthen their overall risk posture. |
What can we expect in 2024 and beyond with DORA?
Timeline for Implementation
The enforcement of DORA is due on January 17th, 2025. Financial entities are required to adhere to the prescribed timelines and prepare for the implementation of DORA requirements.
Expected Changes in the EU Financial Sector
The implementation of DORA is anticipated to bring about significant changes in the EU financial sector, particularly in enhanced operational resilience and security measures. Financial entities are likely to undergo substantial transformations to comply with DORA requirements.
Influence on European Securities and Markets Authority
DORA exerts influence on the European Securities and Markets Authority, as it aligns with the authority's objectives of ensuring the security and resilience of the EU financial system. It enhances the European Securities and Markets Authority's role in overseeing the financial sector's operational resilience.
Overall, the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) represents a pivotal regulatory framework to ensure the financial sector's security and operational resilience within the European Union. With its comprehensive requirements and focus on mitigating ICT-related risks, DORA is set to impact financial entities significantly and enhance the overall resilience of the EU financial system. As financial entities prepare for the implementation of DORA in the coming years, the act is poised to play a transformative role in bolstering the operational resilience of the EU financial sector.
FAQs
DORA, which stands for Digital Operational Resilience Act, is a regulation introduced by the European Union (EU) to enhance the operational resilience of financial entities by focusing on ICT third-party service providers and risk management in the financial sector.
DORA was enacted in 2022 by the European Parliament to address the challenges related to ICT-related incidents and strengthen the resilience testing requirements for financial services.
DORA covers operational risk, network security, information security, and the resilience of EU financial entities, aiming to improve the digital operational resilience of economic entities and ICT third-party service providers.
DORA applies to financial entities and ICT third-party service providers within the EU financial sector, subjecting them to the regulatory requirements and oversight framework established by DORA.
DORA imposes requirements related to resilience testing, financial information security, and the financial sector's operational resilience, ensuring that entities comply with the specified standards to enhance their operational resilience.
Strengthen cyber resilience with an integrated solution

A five-step approach to strengthen your company's cyber resilience, offering key benefits:
- Protect organizations from cyber disruptions
- Comply with cyber resilience regulations
- Align cyber resilience management with business objectives
- Maintain a proactive cyber resilience stance
Governance, Risk and Compliance Related Content
Enhance operational resilience using integrated risk management
MEGA HOPEX for GRC
Request a demonstration of HOPEX for GRC, and see how you can have immediate value of your projects.