Business Architecture vs. Enterprise Architecture: Understanding the Differences and Benefits
Business architecture and enterprise architecture are two terms often used interchangeably, but they have distinct differences. Both fields are important for businesses, and understanding their differences is crucial to successfully implementing them within an organization. Let's explore the difference and how they align with organizational goals.
Differences Between Business Architecture vs. Enterprise Architecture
In Focus: Business Architecture
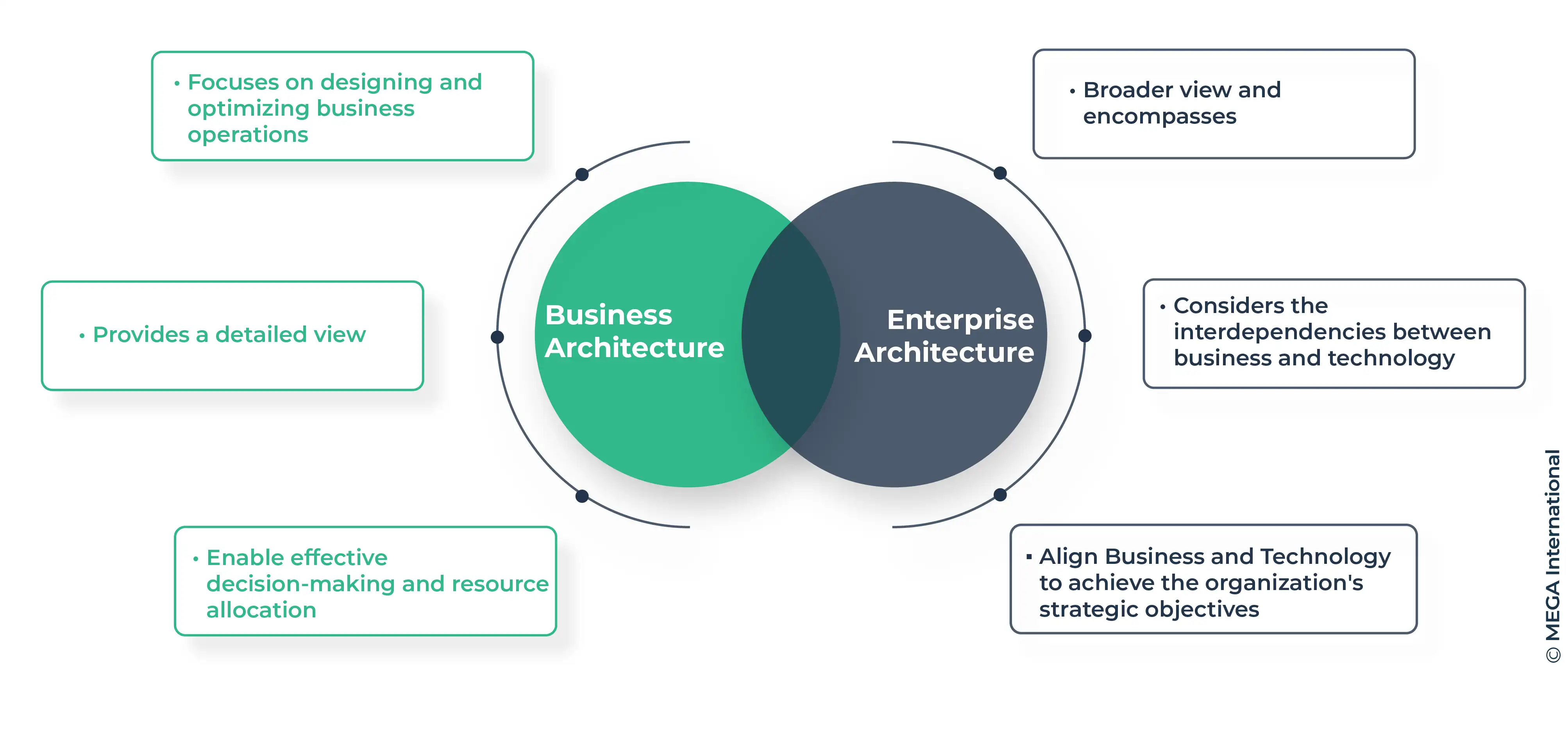
Business architecture primarily focuses on designing and optimizing business operations, including strategy, processes, capabilities, and stakeholders. It provides a detailed view of how the business functions and operates, enabling effective decision-making and resource allocation.
In Focus: Enterprise Architecture
On the other hand, enterprise architecture takes a broader view and encompasses the business aspects, technology infrastructure, and information systems. It considers the interdependencies between business and technology, aiming to align them to achieve the organization's strategic objectives.
Key Components of Business Architecture Vs. Key Components of Enterprise Architecture
Business Architecture
Key components
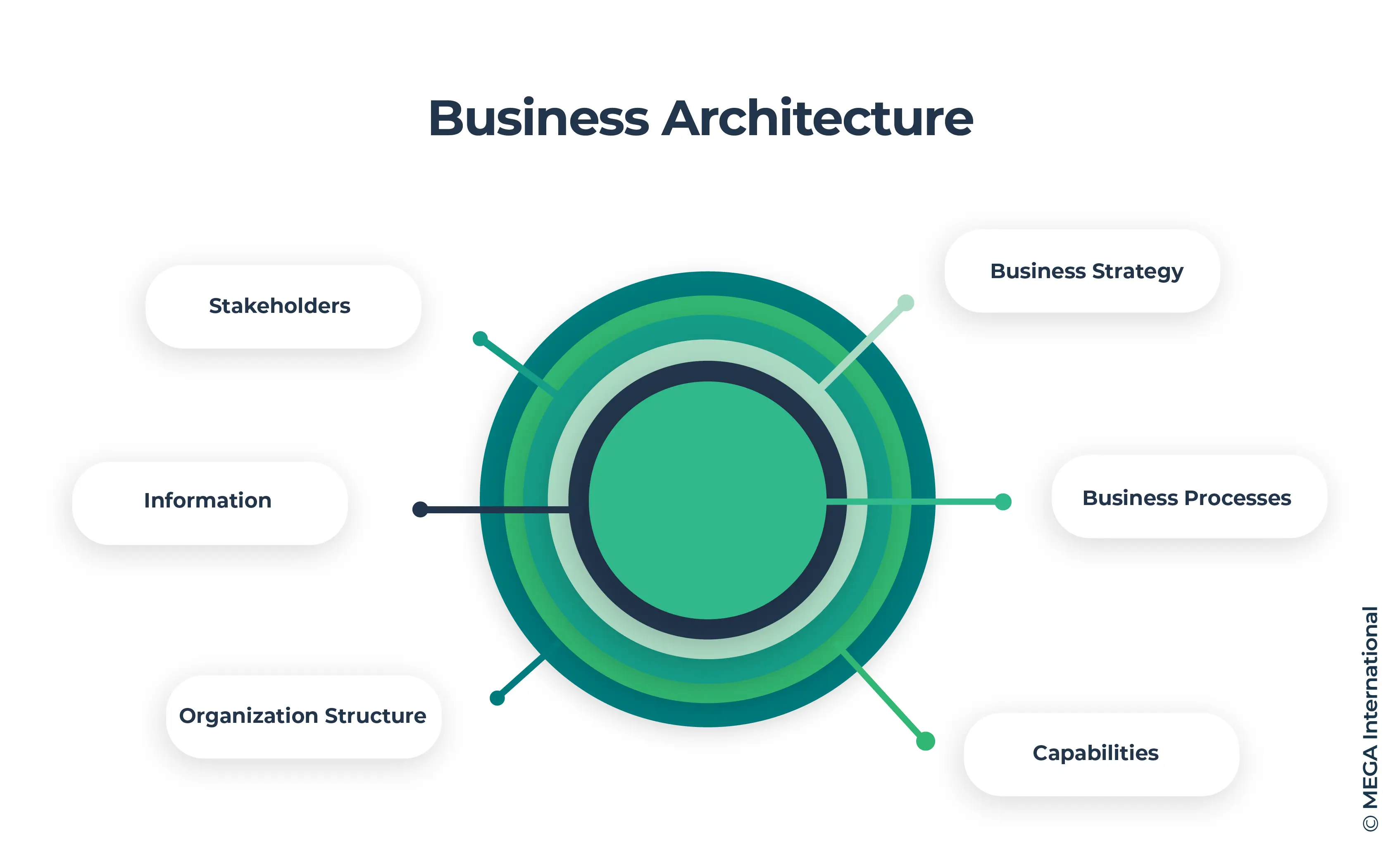
- Business Strategy: Defining the organization's long-term goals, objectives, and competitive positioning.
- Business Processes: Identifying and optimizing the core processes that drive value creation within the organization.
- Capabilities: Understanding the organization's abilities, resources, and competencies required to execute its strategy effectively.
- Information: Managing and leveraging data and information assets to support decision-making and operational processes.
- Organization Structure: Designing the organizational hierarchy, roles, and responsibilities to ensure effective coordination and collaboration.
- Stakeholders: Identifying and engaging with internal and external stakeholders, such as customers, partners, and regulators
Enterprise Architecture
key components
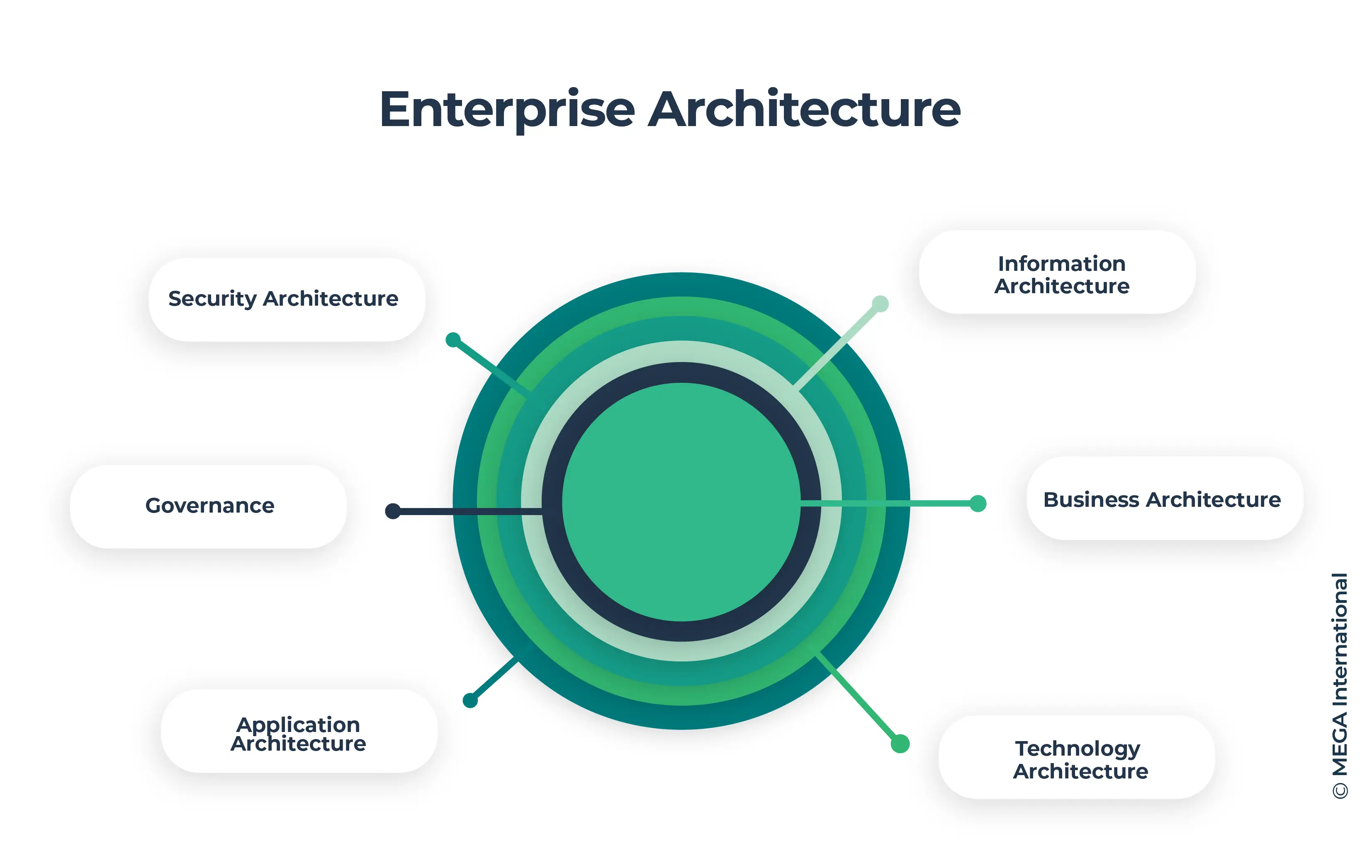
- Business Architecture: Defining the organization's business strategy, processes, capabilities, and stakeholders.
- Information Architecture: Managing and organizing data and information assets, ensuring their availability, integrity, and usability.
- Application Architecture: Identifying and managing the portfolio of applications required to support business operations and enable seamless information flow.
- Technology Architecture: Defining the infrastructure, platforms, and technologies that support the organization's operations and enable efficient IT service delivery.
- Security Architecture: Protecting enterprise assets, information, and systems from internal and external threats.
- Governance: Establishing governance processes and frameworks to guide decision-making, risk management, and compliance.
Relationship and Alignment
Business architecture and enterprise architecture are closely related and should be aligned to ensure maximum effectiveness.
Business architecture defines and transforms an organization's business strategy, capabilities, processes, information, and stakeholders. On the other hand, enterprise architecture provides a holistic view of an organization's business, technology infrastructure, applications, data, networks, and security.
While both frameworks have different perspectives, they are interconnected and should be aligned to maximize their benefits. Business architecture should inform enterprise architecture on the business capabilities and solutions that the organization requires to achieve its strategic goals. This alignment ensures that the IT systems and services that enterprise architecture delivers support the organization's business needs and objectives.
Furthermore, enterprise architecture should inform business architecture about the organization's technological capabilities and limitations. This shared understanding of the organization's technology landscape enables business architects to design feasible, cost-effective, scalable solutions and capabilities.
Business and enterprise architecture are essential to a modern, agile, customer-focused organization. They aim to provide an aligned and integrated understanding of an organization's operations. Therefore, aligning both frameworks to give the organization a harmonious and compelling architecture is necessary.
Roles and Responsibilities
Regarding roles and responsibilities, business architects are primarily responsible for designing and optimizing business processes, capabilities, and stakeholders. They work closely with business stakeholders to define the organization's strategic goals and ensure the business architecture supports them.
On the other hand, enterprise architects are responsible for designing and aligning the organization's technology infrastructure, information systems, and applications. They work closely with IT teams, vendors, and other stakeholders to ensure that the enterprise architecture enables efficient and effective technology solutions that support the business architecture.
Learn More About Enterprise Architecture
Elements of Business Architecture and Enterprise Architecture
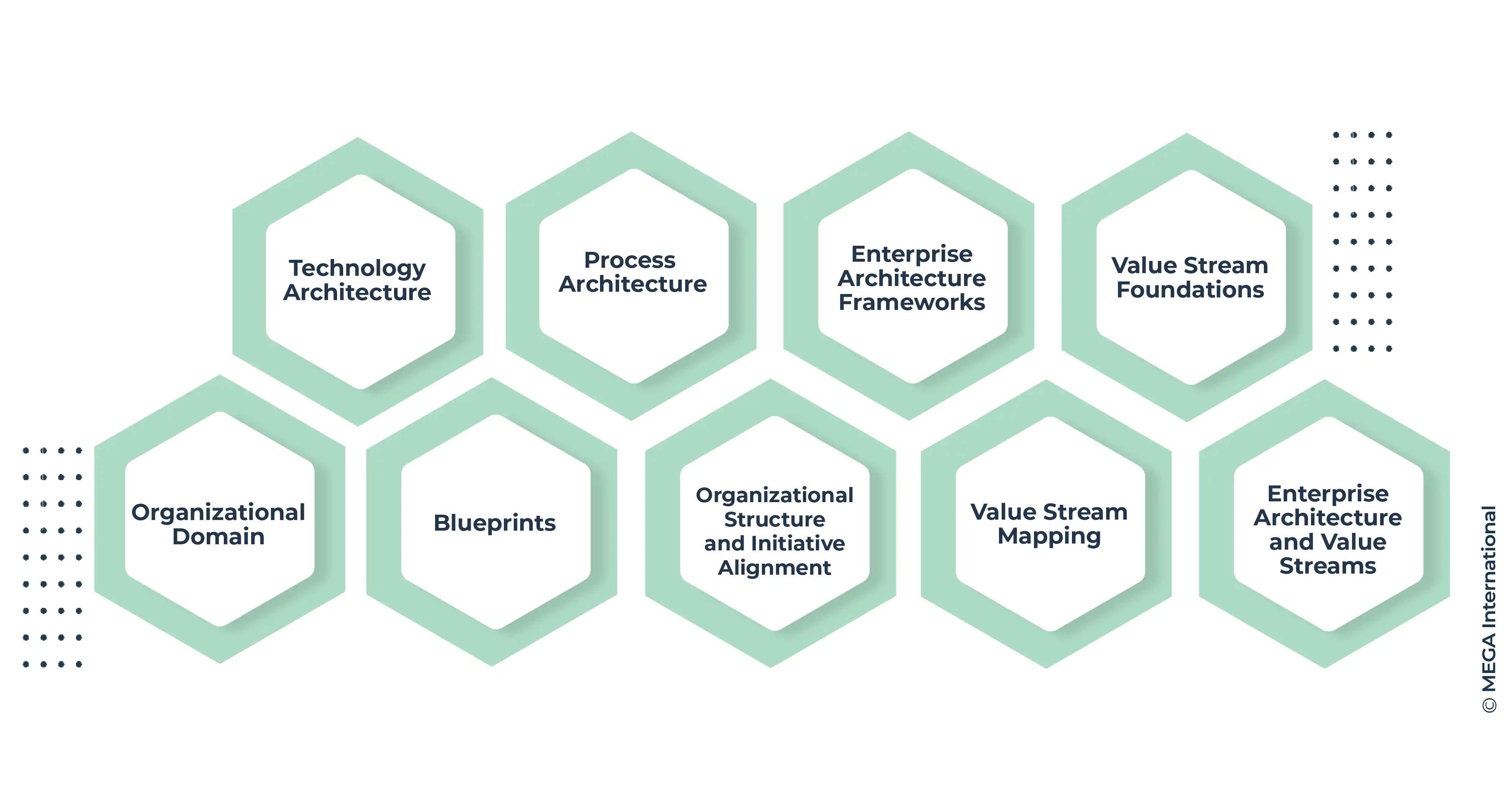
Technology Architecture
A subset of enterprise architecture focuses on an organization's technology infrastructure. Enterprise architects work with technology architects to define the hardware, software, and network requirements that support business operations. Technology architecture must be aligned with business objectives to ensure that technology provides maximum value to the organization.
Process Architecture
Process architecture is another subset of enterprise architecture that focuses on the design and structure of business processes. Enterprise architects work with business analysts to identify inefficiencies in business processes and design solutions that streamline operations. By improving process architecture, organizations can improve efficiency and reduce costs.
Enterprise Architecture Frameworks
Enterprise architecture frameworks provide a structured approach to designing and implementing enterprise architecture. The Zachman Framework and TOGAF are two popular enterprise architecture frameworks that guide aligning business and technology. These frameworks define a standard language and methodology for implementing enterprise architecture.
Organizational Domain
Business architecture focuses on the design and structure of an organization's business processes, while enterprise architecture focuses on the organization, including business processes, technology, and data. Sometimes, Business architecture pertains to a specific business unit or function, while enterprise architecture spans the entire organization.
Blueprints
Business architecture provides a blueprint for how a business operates, while enterprise architecture provides a blueprint for how technology supports business operations. Business architecture defines a company's components and how they work together, while enterprise architecture defines how technology helps business functions.
Organizational Structure and Initiative Alignment
Business architecture defines the structure and organization of a business unit or function, while enterprise architecture defines the structure and organization of an entire enterprise. Business architecture ensures that an organization's initiatives align with business objectives, while enterprise architecture ensures that technology initiatives align with business objectives.
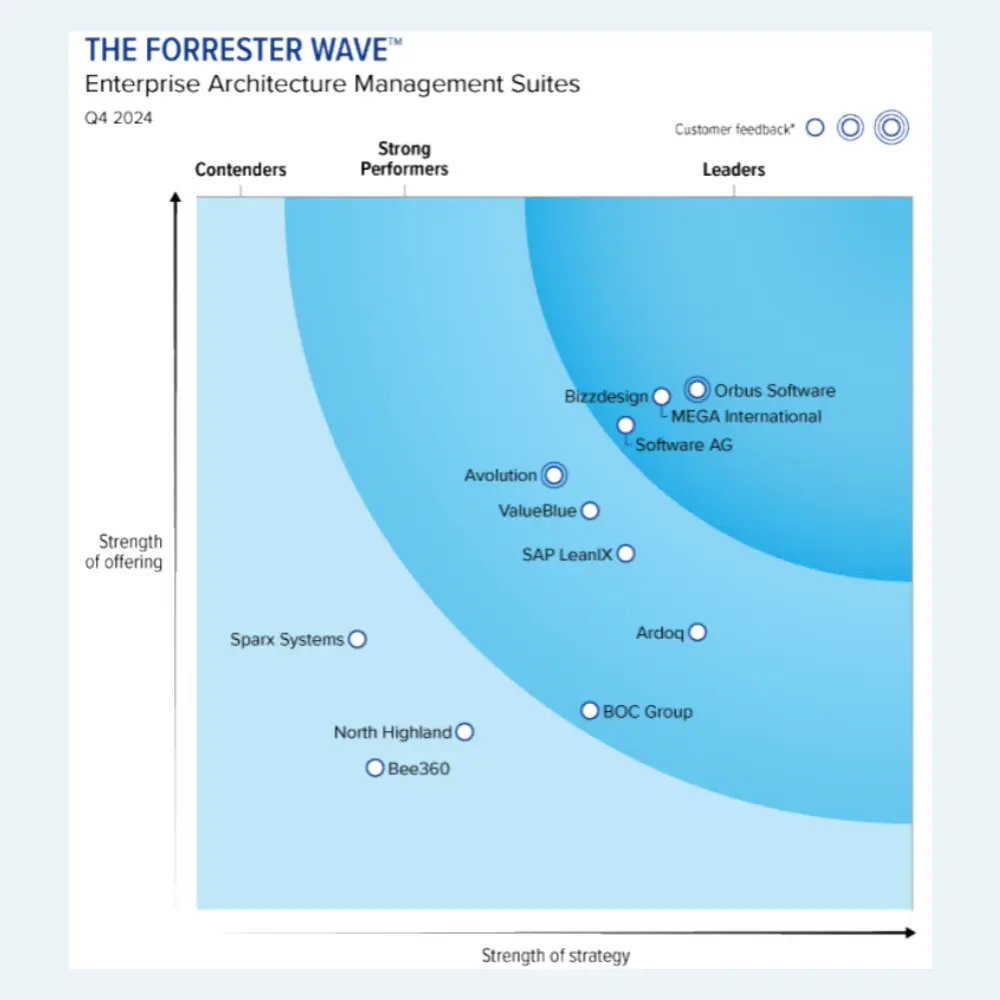
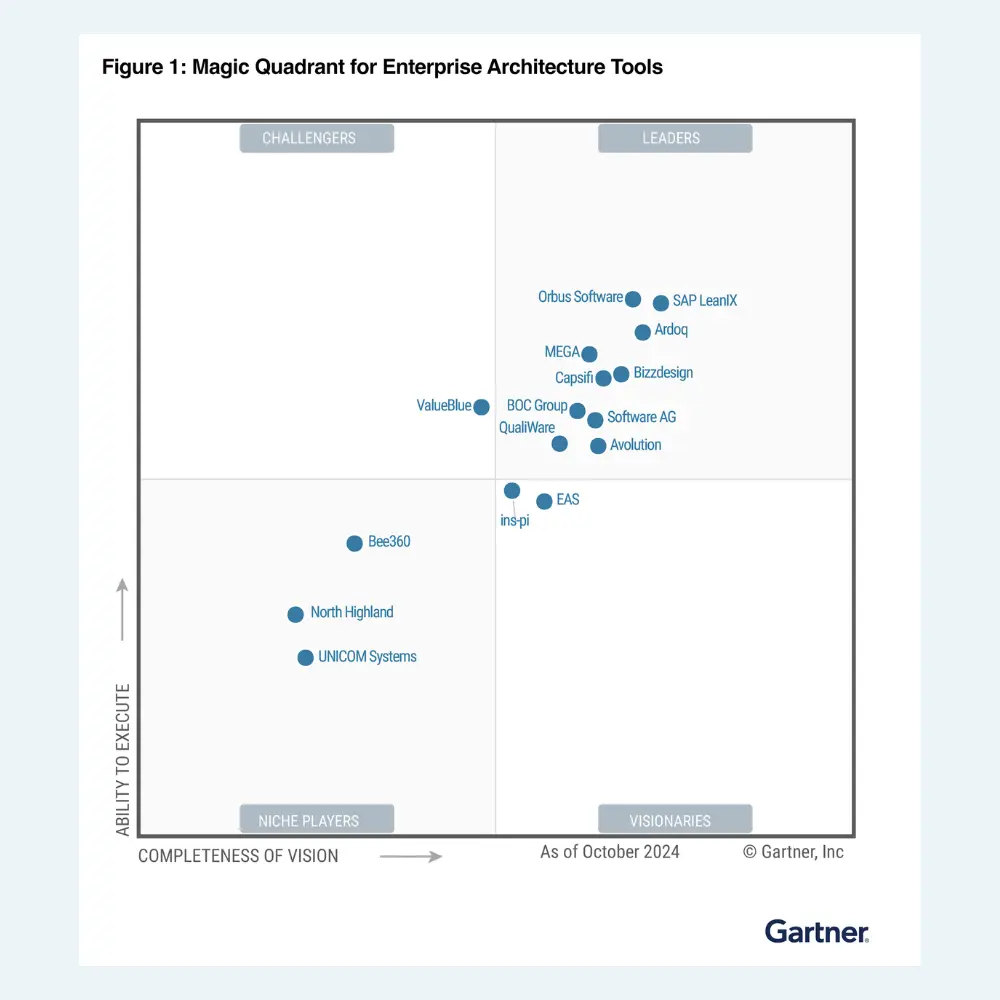
Get a complimentary copy: 2024 Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Enterprise Architecture Tools
Value Stream Mapping
Value stream mapping is a process for identifying inefficiencies in business processes. It involves mapping out how business activities are performed, identifying waste areas, and developing a plan for eliminating waste. Value stream mapping is an important tool for enterprise architects to identify areas of inefficiency in business processes that can be targeted for improvement.
Value Stream Foundations
Value stream foundations are the fundamental components of a business that contribute to its value stream. These include people, processes, and technology. Enterprise architects evaluate value stream foundations to ensure that they are aligned with business objectives and recommend changes as necessary.
Enterprise Architecture and Value Streams
Enterprise architecture supports value streams by ensuring that technology is aligned with business objectives. By identifying inefficiency in business processes and developing solutions that streamline operations, enterprise architects help businesses achieve their goals. Value stream mapping and value stream foundations provide enterprise architects with a comprehensive understanding of how a company operates and where improvements can be made.
Benefits of Business Architecture and Enterprise Architecture
As mentioned, Business architecture and enterprise architecture are two important frameworks for managing organizations and their processes. Business architecture provides a blueprint for organizational strategy, structure, and operations, while enterprise architecture expands this view to include technology and information. Both frameworks offer numerous benefits for organizations that embrace them.
Read: Enterprise Architecture Strategy
For one, they help align business strategies and goals with IT strategies and capabilities, ensuring that technology investments are aligned with business needs. They can also help identify opportunities for standardization and consolidation, streamlining operations, and reducing costs.
Summary
Business and enterprise architecture are essential for companies to achieve their goals and remain competitive. Business architecture defines the design and structure of business processes, while enterprise architecture spans the entire organization, including business processes, technology, and data.
By understanding the differences between business architecture and enterprise architecture, businesses can develop a comprehensive strategy for achieving their objectives and staying ahead of the competition.
FAQs
Business Architecture designs and documents business aspects such as strategy, processes, capabilities, and organization. In contrast, Enterprise Architecture encompasses a broader scope, including technical and information architecture and business architecture, enabling the organization to align its business and IT goals.
Business Architect is responsible for designing and documenting the business value chain, business capability architecture, business processes, and business stakeholders. They focus on utilizing the business architecture domain to achieve the organization's goals.
An Enterprise Architect is responsible for designing and implementing enterprise architecture components, including business design, technology architecture, and application architecture. They ensure that all enterprise architecture components are aligned with the organization's objectives and work towards improving the architecture practice within the enterprise. Learn more about The Role of Enterprise Architect.
An architecture framework provides the blueprint of the enterprise, and it outlines the architecture domain in which the organization operates. It offers the necessary structure to design, document, and deploy effective architectural solutions that meet the business's objectives. Learn more about Enterprise Architecture Framework.
Technology Architecture is a component of Enterprise Architecture that defines the principles, standards, and guidelines for implementing and managing technology infrastructure within an organization.
Business Architects are responsible for clearly understanding how an existing business operates. At the same time, Enterprise Architects create and maintain a conceptual and technical view of the enterprise that provides a common understanding of the business functions, processes, and underlying technology.
Enterprise Architecture Framework focuses on aligning all the components within an organization, while Business Architecture framework focuses on the business value.
Business Architects are responsible for designing and documenting the organization's business aspects. At the same time, Enterprise Architects are responsible for the design and implementation of all components of enterprise architecture, including business architecture.
Business Architect's target audiences are business executives, stakeholders, middle-management, and operational staff. Enterprise Architects' target audiences are IT executives, IT staff, security personnel, procurement personnel, and business stakeholders.
Benefits of using Business Architecture include more effective business strategies, increased efficiency and productivity, reduced ambiguity in communication, and more effective measurement of business performance. Benefits of using Enterprise Architecture include more effective alignment between different departments, more effective use of resources, a more agile and forward-looking IT department, and a better ability to leverage emerging technologies.
Yes, both business architecture and enterprise architecture can be applied in various industries, including but not limited to finance, healthcare, manufacturing, and technology. The principles and methodologies can be tailored to suit different industries' specific needs and requirements.
While organizations don't need to have dedicated roles for business and enterprise architects, having specialized professionals can significantly contribute to the effectiveness of these frameworks. They bring expertise and knowledge that can drive successful implementation and ensure the optimal alignment of business and technology.
Various online resources, including books, articles, and industry-specific publications, provide in-depth insights into business and enterprise architecture. Additionally, attending conferences, workshops, and professional training programs by MEGA International can help you and organizations comprehensively understand these frameworks and their applications.
Business Architecture and Enterprise Architecture work together to create a comprehensive and holistic view of an organization. Business Architecture focuses on a business model's structure, operations, and governance. In contrast, Enterprise Architecture focuses on how an organization can align its technology and processes with overall business strategy and value streams. They can help an organization create a more cohesive and effective operational environment.
Bridge the Gap Between Strategy and Execution

Build a Strong Business Architecture and IT Architecture Alignment.
One must consider five principles to achieve business and IT architecture alignment. This white paper will further explore these topics and provide key steps for aligning business and IT architecture.
Enterprise Architecture Related Content
Shift from a documentation tool to an operational tool and accelerate business transformation
MEGA HOPEX for Enterprise Architecture
Request a demonstration of HOPEX for EA, and see how you can have immediate value of your projects.