Business Architecture Strategy: Building a Strong Foundation for Organizational Success
A well-defined Business Architecture Strategy is a critical framework for aligning business operations with strategic objectives, ensuring that all enterprise components work cohesively towards common goals.
Business architecture strategy involves aligning enterprise architecture with an organization's goals to drive value and achieve strategic business outcomes. It encompasses business, process, technology, and solution architecture.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to mastering Business Architecture Strategy. We will explore its key components, the steps involved in developing a robust strategy, the tools and frameworks available, and the challenges organizations might face during implementation. Additionally, we will highlight the benefits of a well-defined Business Architecture Strategy through real-world case studies and examine future trends shaping this critical field.
What is Business Architecture, and How Does it Impact Strategies?
Business Architecture is a structured discipline that comprehensively views an organization's structure and operations. It bridges the gap between strategic planning and operational execution by outlining how various business components interact and align with the company's goals. The scope of Business Architecture encompasses the enterprise's entire ecosystem, including its organizational structure, business processes, information flow, and technological infrastructure.
Steps to Develop a Business Architecture Strategy
Developing a comprehensive Business Architecture Strategy involves several critical steps. Each step ensures that the strategy aligns with organizational goals, addresses current challenges, and lays a clear path for future growth and adaptation.
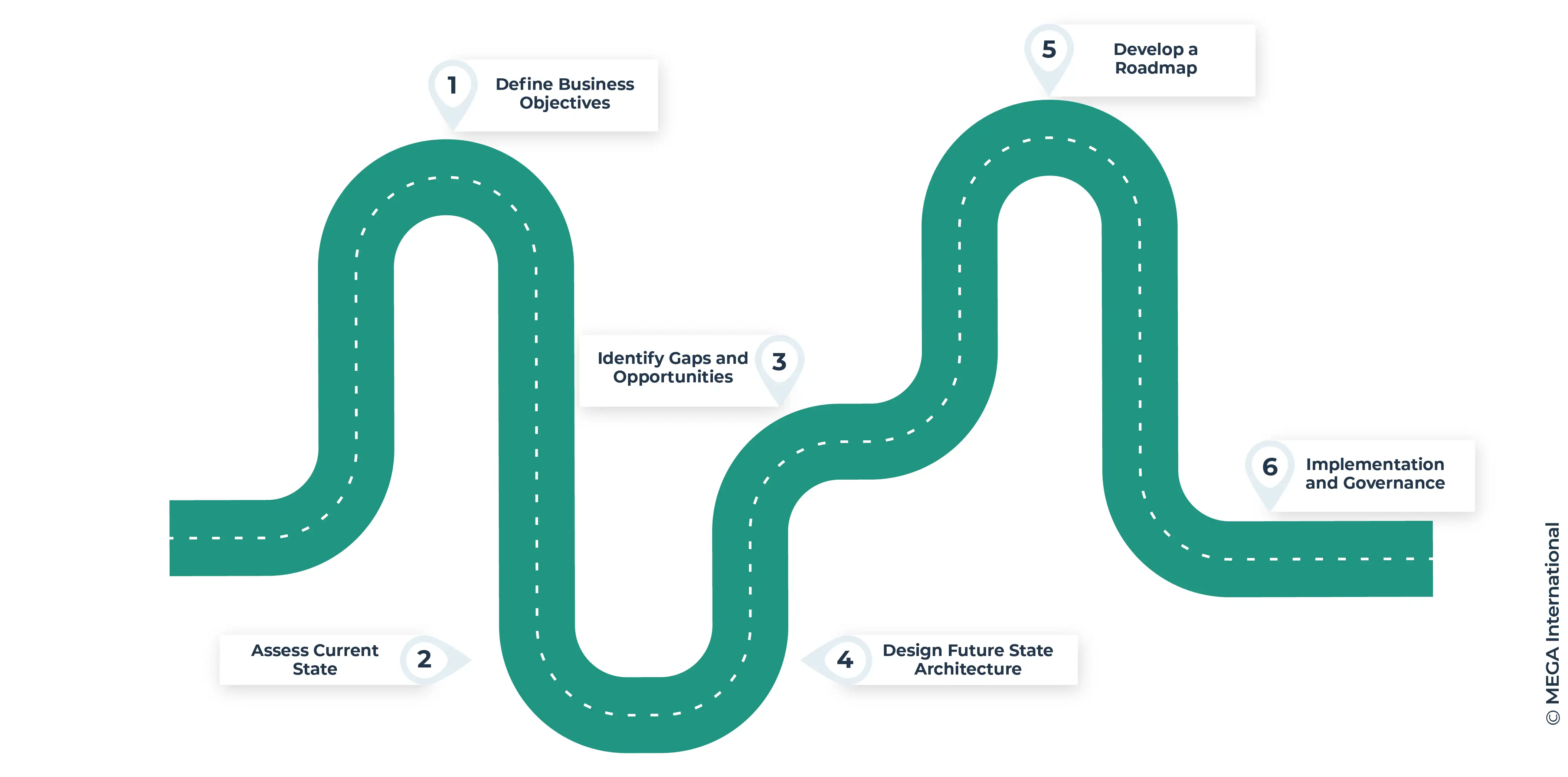
Step 1: Define Business Objectives
Identifying Goals and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):
- Begin by clearly defining the organization’s strategic goals and objectives. These should be aligned with the company's overall vision and mission.
- Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure progress toward these goals. KPIs should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
Step 2: Assess Current State
Analyzing Existing Architecture:
- Conduct a thorough assessment of the current business architecture, including organizational structure, processes, information flow, and IT infrastructure.
- Gather input from stakeholders across the organization to comprehensively view the existing architecture’s strengths and weaknesses.
- Document the current state using visual tools like diagrams and models to create a clear and accessible representation.
Step 3: Identify Gaps and Opportunities
Gap Analysis Techniques:
- Perform a gap analysis to identify discrepancies between the current and desired future states. This involves comparing current capabilities, processes, and structures with the organization’s strategic objectives.
- Identify opportunities for improvement and areas where new capabilities or changes are needed to achieve business goals.
- Use techniques such as SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) to systematically evaluate gaps and opportunities.
Step 4: Design Future State Architecture
Blueprint for Future Architecture:
- Develop a detailed blueprint for the future state of the business architecture. This blueprint should outline the desired organizational structure, processes, information flow, and technology infrastructure.
- Ensure that the future state design aligns with the organization’s strategic goals and addresses the gaps and opportunities identified in the previous step.
- Create detailed models and diagrams to visualize the future state and facilitate stakeholder communication.
Step 5: Develop a Roadmap
Prioritization and Timelines:
- Develop a strategic roadmap outlining the steps needed to transition from the current state to the future. This roadmap should include prioritized initiatives, timelines, and milestones.
- Prioritize initiatives based on their impact on business goals, feasibility, and resource availability.
- Establish clear timelines and milestones to track progress and ensure accountability.
Step 6: Implementation and Governance
Execution Plan and Governance Framework:
- Develop a detailed execution plan outlining the actions, responsibilities, and resources required to implement the business architecture strategy.
- Establish a governance framework to oversee the implementation process. This framework should include roles and responsibilities for key stakeholders, decision-making processes, and mechanisms for monitoring and controlling progress.
- Implement regular review and feedback loops to ensure that the strategy remains aligned with business goals and can adapt to changing circumstances.
| This structured approach ensures that all business components work together cohesively to achieve long-term success. business components |
Tool: Process Management
Tools and Frameworks for Business Architecture Strategy
Developing and implementing a Business Architecture Strategy requires various tools and frameworks that provide structure, methodology, and best practices. Here are some of the most popular tools and frameworks used in the field:
Popular Tools
ArchiMate:
ArchiMate is an open and independent modeling language for enterprise architecture. It provides a uniform representation for diagrams that describe enterprise architectures, making it easier to understand complex structures and relationships.
ArchiMate supports various views, including business, application, and technology layers, which helps visualize the alignment between business goals and IT infrastructure.
TOGAF (The Open Group Architecture Framework):
TOGAF is a comprehensive framework for designing, planning, implementing, and governing enterprise information architecture. It provides a detailed methodology and tools for developing an enterprise architecture that aligns with business objectives.
The TOGAF Architecture Development Method (ADM) guides creating and managing an enterprise architecture, ensuring all aspects of the organization are covered.
BIZBOK (Business Architecture Body of Knowledge)
BIZBOK provides a comprehensive guide to best practices for business architecture. It covers various topics, including capability mapping, value stream mapping, and organizational mapping.
| BIZBOK is widely recognized for its detailed and practical approach, making it a valuable resource for business architects. |
Sparx Systems Enterprise Architect:
This potent modeling tool supports various frameworks and modeling languages, including UML, BPMN, and ArchiMate. It provides a collaborative environment for developing and managing business architecture models.
The tool offers extensive project management, simulation, and code engineering features, making it versatile for different stages of architecture development.
Challenges in Implementing Business Architecture Strategy
Implementing a Business Architecture Strategy is a complex endeavor that encounters several challenges. Understanding these common obstacles and learning how to overcome them can significantly improve the chances of a successful implementation.
Common Obstacles and How to Overcome Them
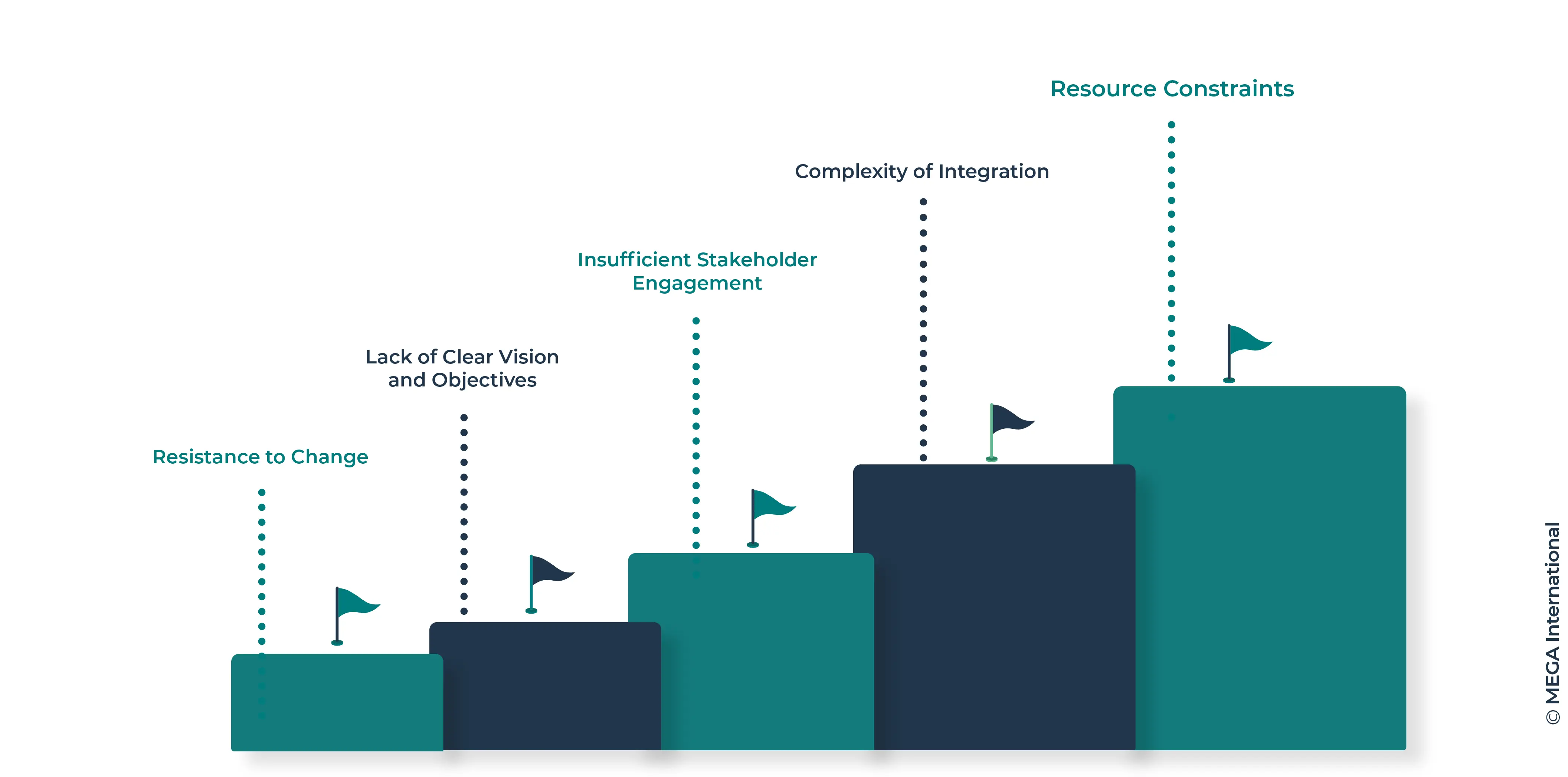
Resistance to Change:
Challenge
Employees and stakeholders may resist changes due to fear of the unknown, loss of control, or comfort with the current state.
Solution
To overcome resistance, involve stakeholders early in the process, communicate the benefits clearly, and provide training and support. Engaging key influencers within the organization can also help foster a culture that embraces change.
Lack of Clear Vision and Objectives:
Challenge
The business architecture strategy can become unfocused and ineffective without a clear vision and well-defined objectives.
Solution
Establish a clear vision and specific, measurable objectives. Ensure that these goals are communicated effectively across the organization and that all stakeholders understand their role in achieving them.
Insufficient Stakeholder Engagement:
Challenge
Limited engagement from key stakeholders can lead to a lack of buy-in and support, undermining the strategy’s success.
Solution
Foster strong stakeholder engagement by involving them in the planning and decision-making. Regular updates, feedback sessions, and transparent communication can help maintain their interest and commitment.
Complexity of Integration
Challenge
Integrating new architecture with existing systems and processes can be highly complex and prone to issues.
Solution
Conduct thorough assessments of existing systems and develop a detailed integration plan. Use phased implementation to manage complexity and ensure proper testing and validation at each stage.
Resource Constraints
Challenge
Limited resources, including time, budget, and skilled personnel, can hinder implementation.
Solution
Prioritize initiatives based on their strategic importance and feasibility. Allocate resources efficiently and consider leveraging external expertise or partnerships to supplement internal capabilities.
Real-World Examples
Example: Resistance to Change in a Manufacturing Company
Scenario
A manufacturing company faced significant resistance from its workforce when implementing a new business architecture strategy to automate critical processes.
Resolution
The company addressed this by conducting workshops to educate employees on the benefits of automation, providing training sessions, and setting up a support system to help staff transition smoothly. This approach helped reduce resistance and facilitated a smoother implementation process.
Example: Lack of Clear Vision in a Financial Institution
Scenario
A financial institution struggled with implementing its business architecture strategy due to a lack of clear vision and objectives.
Resolution
The institution reassessed its strategy and engaged an external consultant to help define a clear vision and set achievable objectives. This renewed focus provided direction and clarity, improving stakeholder alignment and execution.
Benefits of a Well-Defined Business Architecture Strategy
A well-defined Business Architecture Strategy offers numerous advantages that can significantly enhance an organization's overall performance and competitive edge. Here are some of the key benefits:
Improved Decision-Making
- Enhanced Insights: A well-defined business architecture provides a comprehensive view of the organization’s structure, processes, and capabilities, enabling leaders to make informed decisions.
- Data-Driven Strategies: With precise and accurate data flow and information management, organizations can base their strategies on reliable data, leading to better outcomes.
Better Alignment Between Business and IT
- Strategic Cohesion: Aligning IT infrastructure with business goals ensures that technology investments directly support strategic objectives, leading to more effective use of resources.
- Increased Agility: By ensuring that business processes and IT systems are closely aligned and flexible, organizations can quickly adapt to changes in the market or industry.
Enhanced Operational Efficiency
- Streamlined Processes: Identifying and optimizing key business processes reduces redundancy and inefficiencies, leading to smoother operations and cost savings.
- Improved Resource Utilization: A well-defined business architecture helps in optimizing the use of resources, including human capital, technology, and financial investments.
Effective Change Management
- Structured Approach: Provides a clear roadmap for implementing changes, ensuring smooth and well-managed transitions.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Facilitates better communication and involvement of stakeholders in the change process, increasing buy-in and reducing resistance.
Greater Business Agility and Scalability
- Adaptability: Organizations can more easily pivot in response to new opportunities or challenges, thanks to a flexible and responsive business architecture.
- Scalability: As the business grows, the architecture can be scaled accordingly, supporting new products, services, or market expansions without significant disruptions.
Improved Customer Experience
- Enhanced Service Delivery: Streamlined processes and efficient use of technology lead to better and more consistent customer service.
- Personalization: A clear understanding of business capabilities and data flows enables more personalized and targeted customer interactions.
Risk Management and Compliance
- Risk Mitigation: Identifying and addressing potential risks within the business architecture helps mitigate issues before they escalate.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensures that business processes and data management practices adhere to relevant laws and regulations, reducing the risk of non-compliance penalties.
Innovation and Growth
- Fostering Innovation: By clearly defining business capabilities and processes, organizations can more easily identify areas for innovation and improvement.
- Supporting Growth: A robust business architecture supports strategic growth initiatives, helping organizations expand and enter new markets effectively.
Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
- Unified Framework: Provides a common language and framework for different departments and teams to collaborate effectively.
- Transparency: Clear documentation and visualization of business architecture facilitate better communication and understanding across the organization.
Long-Term Sustainability
- Strategic Alignment: Ensures that all parts of the organization work towards common long-term goals, fostering sustained growth and success.
- Continuous Improvement: A well-defined business architecture promotes a culture of constant improvement, where processes and systems are regularly evaluated and optimized.
These benefits collectively contribute to an organization’s ability to remain competitive and thrive in a constantly evolving business environment.
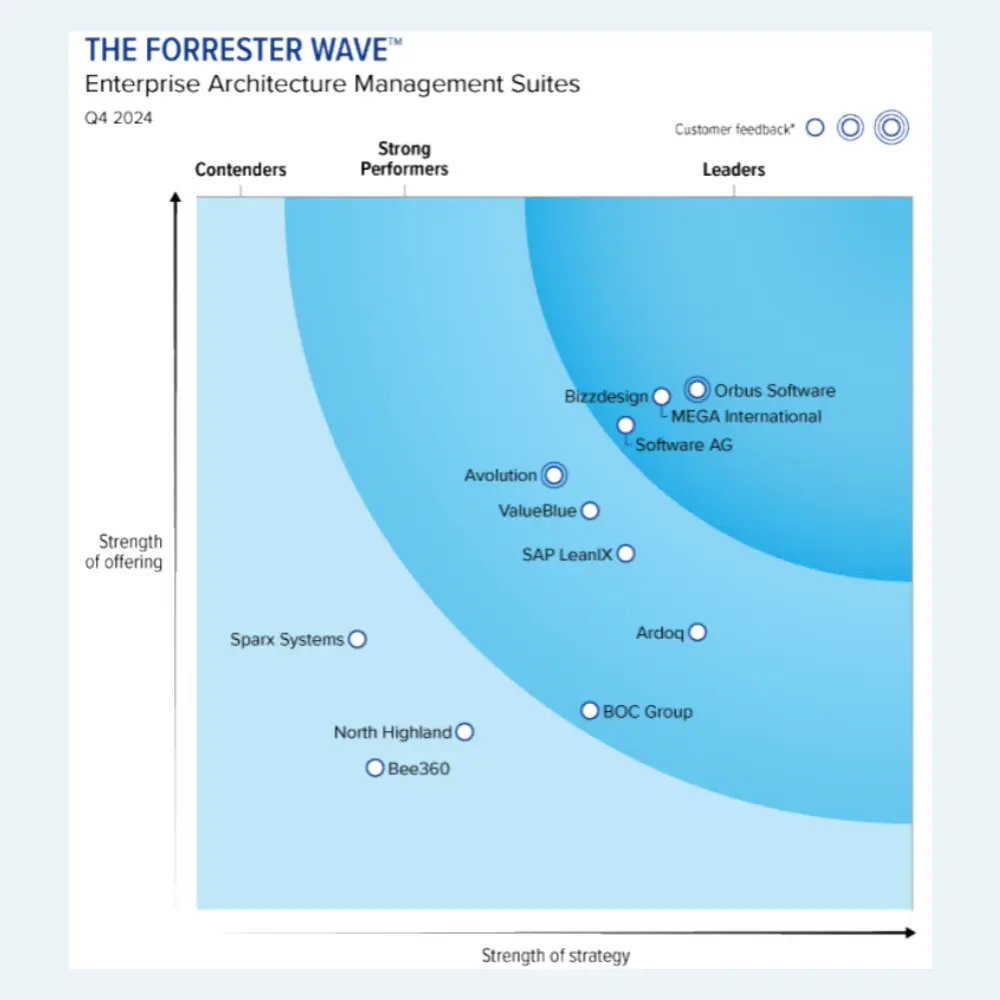
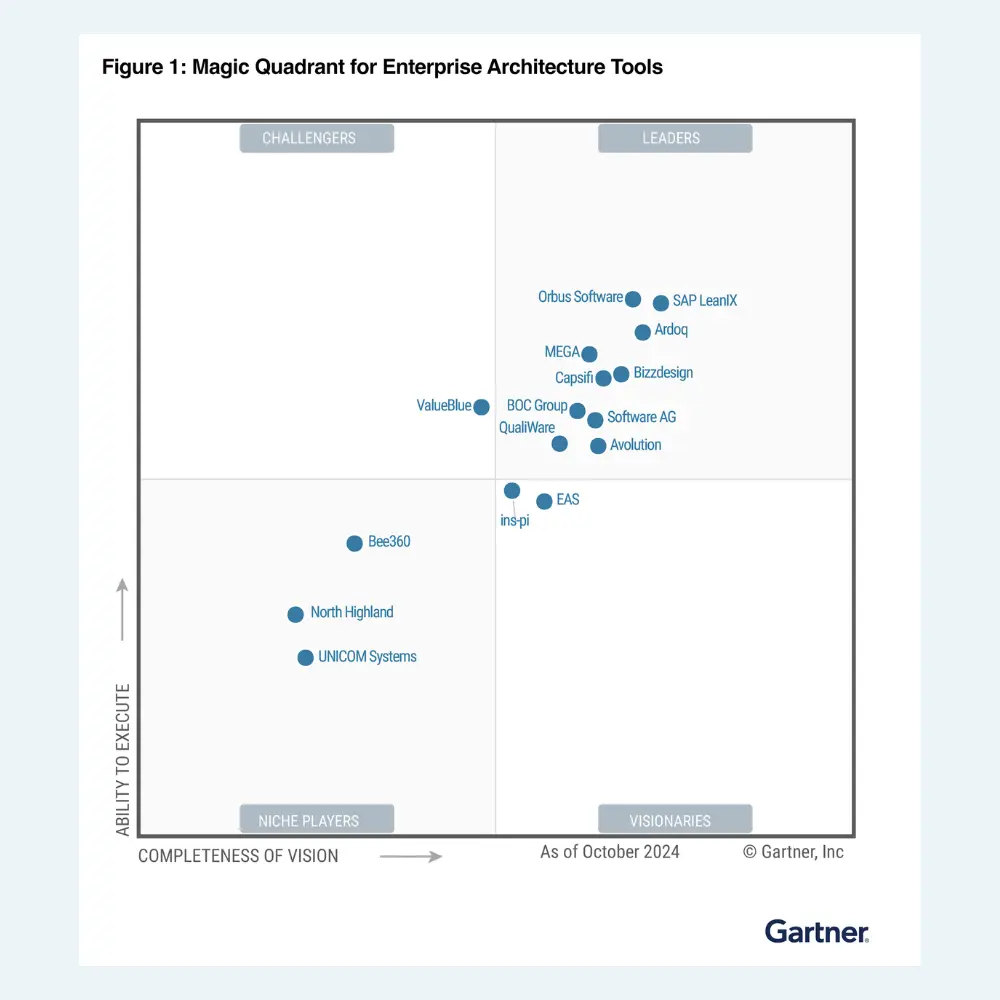
Get a complimentary copy: 2024 Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Enterprise Architecture Tools
Case Studies and Success Stories
Understanding how real-world organizations successfully implement Business Architecture Strategies can provide valuable insights and inspiration. Here are a few examples of companies that have effectively leveraged business architecture to achieve their goals, as well as key takeaways and lessons learned.
Case Study 1: Global Retail Chain
Scenario: A global retail chain faced operational inefficiencies and inconsistent customer experiences. To address these issues, the company implemented a comprehensive Business Architecture Strategy.
Implementation:
|
Results:
- Improved operational efficiency through standardized processes and optimized resource utilization.
- Enhanced customer satisfaction with consistent and personalized service across all locations.
- Significant reduction in operational costs due to better inventory management and streamlined supply chain processes.
Key Takeaways:
- A comprehensive assessment of current state architecture is crucial for identifying inefficiencies and areas for improvement.
- Capability mapping helps in understanding and prioritizing essential business functions.
- Phased implementation and strong governance are essential for successful execution and minimizing disruption.
Case Study 2: Financial Services Company
Scenario: A financial services company struggled with outdated systems and siloed operations, which hindered its ability to respond to market changes and regulatory requirements. The company embarked on a business architecture strategy to modernize its operations and improve agility.
Implementation:
|
Results:
- Increased agility in responding to market changes and regulatory requirements.
- Enhanced service delivery through the adoption of modern technologies.
- Improved collaboration and communication across departments, leading to more cohesive operations.
Key Takeaways:
- Aligning business architecture with the organization's vision is critical for driving strategic initiatives.
- Modern technologies can significantly enhance business capabilities and agility.
- Strong stakeholder engagement is essential for successful implementation and buy-in.
Case Study 3: Healthcare Provider
Scenario: A large healthcare provider aimed to improve patient care and operational efficiency by implementing a Business Architecture Strategy. The organization needed to integrate disparate systems and streamline processes across multiple facilities.
Implementation:
|
Results:
- Enhanced patient care through integrated and efficient processes.
- Reduced administrative burden and improved operational efficiency.
- Better data management and reporting capabilities, leading to improved compliance and decision-making.
Key Takeaways:
- Process mapping is vital for identifying and addressing inefficiencies.
- Integrated systems can significantly improve service delivery and operational efficiency.
- A robust change management plan is essential for supporting staff and ensuring smooth transitions.
These case studies highlight the significant benefits and critical lessons from successfully implementing Business Architecture Strategies.
Future Trends in Business Architecture
Business Architecture must adapt to emerging trends and technologies as the business environment evolves. Understanding these trends can help organizations stay ahead of the curve and maintain a competitive edge. Here are some of the key emerging trends and predictions for the future of Business Architecture:
Emerging Trends and Technologies
Digital Transformation:
Digital transformation remains a significant driver of change in Business Architecture. Organizations increasingly leverage digital technologies to streamline operations, enhance customer experiences, and drive innovation.
Key technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and the Internet of Things (IoT) are becoming integral parts of business strategies, enabling data-driven decision-making and operational efficiencies.
Cloud Computing:
The adoption of cloud computing continues to grow, offering businesses scalable, flexible, and cost-effective solutions for their IT infrastructure needs.
Cloud-based platforms and services enable organizations to quickly adapt to changing business requirements, enhance collaboration, and improve data accessibility and security.
Business Ecosystems:
The concept of business ecosystems, where companies collaborate and co-create value with partners, suppliers, and customers, is gaining traction.
Business Architecture must now account for these extended networks, focusing on integration, interoperability, and seamless communication between various stakeholders.
Customer-Centricity:
A shift towards customer-centric business models is influencing Business Architecture. Organizations prioritize customer experiences and engagement, using data analytics and insights to tailor products and services to customer needs.
Business Architecture strategies are evolving to emphasize understanding and enhancing the customer journey.
Predictions for the Future
Increased Automation:
Automation will become more prominent in business processes, driven by AI, robotics, and cognitive technology advancements. Organizations will increasingly automate routine tasks, allowing human resources to focus on higher-value activities.
Business Architecture must integrate automation seamlessly into workflows and ensure that automated systems align with business goals.
Greater Emphasis on Sustainability:
Sustainability and environmental responsibility will become central to business strategies. Organizations will seek to incorporate sustainable practices into their operations and value chains.
Business Architecture must support sustainability initiatives, ensuring business processes and systems are designed to minimize environmental impact.
Enhanced Cybersecurity:
As cyber threats become more sophisticated, cybersecurity will be a critical concern for organizations. Business Architecture strategies must incorporate robust security measures to protect sensitive data and ensure compliance with regulations.
The focus will be on creating resilient architectures that can withstand and quickly recover from cyber incidents.
Integration of Emerging Technologies:
Emerging technologies such as blockchain, augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR) will find more applications in business operations. These technologies will enable new business models, improve transparency, and enhance customer experiences.
Business Architecture must accommodate these technologies, ensuring they are integrated effectively and aligned with strategic objectives.
Data-Driven Decision Making:
The proliferation of big data and advanced analytics will drive more organizations to adopt data-driven decision-making processes. Business Architecture must ensure data is accurately captured, processed, and analyzed to inform strategic decisions.
Predictive analytics and real-time data insights will become essential tools for business leaders.
Personalization and Customization:
As consumers increasingly demand personalized experiences, businesses will focus on customizing their offerings to meet individual preferences. Business Architecture must support personalization at scale, leveraging data analytics and flexible processes.
This trend will drive the need for modular and adaptable business architectures that quickly respond to changing customer needs.
How Hopex can help with Business Architecture Strategy
HOPEX is a powerful enterprise architecture tool that can significantly enhance your Business Architecture Strategy. Here’s how Hopex can assist in various aspects of developing and implementing an effective strategy:

1. Comprehensive Modeling and Visualization
Unified Repository: Hopex provides a centralized repository for all business architecture artifacts, ensuring consistency and easy access to information across the organization.
Visual Modeling: Create detailed visual models of your business architecture, including business processes, capabilities, organizational structures, and IT infrastructure.
2. Business Capability Mapping
Capability Identification: Use Hopex to identify and map the core business capabilities required to achieve your strategic objectives. This helps in understanding what the business does and how it does it.
Gap Analysis: Perform capability-based gap analysis to identify discrepancies between current capabilities and future state requirements, highlighting areas for improvement and investment.
3. Strategic Alignment
Goal Alignment: Use Hopex's strategic planning features to align business architecture with strategic goals. Define and link business objectives, capabilities, and IT initiatives to ensure cohesive and aligned operations.
Roadmap Development: Develop strategic roadmaps that outline the steps needed to transition from the current state to the future. Hopex helps prioritize initiatives and set timelines to achieve strategic goals effectively.
4. Process Optimization
Process Mapping: Document and analyze existing business processes to identify inefficiencies and bottlenecks. Hopex allows for detailed process mapping and workflow analysis.
Optimization and Automation: Use insights gained from process analysis to streamline operations, eliminate redundancies, and automate routine tasks, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
5. Change Management
Impact Analysis: Conduct an impact analysis to understand the effects of changes on different parts of the organization. HOPEX provides tools to assess the impact of changes on processes, capabilities, and IT systems.
Communication and Training: Facilitate effective communication and training plans using HOPEX’s change management features, ensuring all stakeholders are prepared for transitions.
6. Risk Management and Compliance
Risk Identification: Identify and document business processes and IT systems risks. HOPEX's robust risk management features help assess and mitigate these risks.
Compliance Management: Ensure compliance with industry regulations and standards by using HOPEX to track and manage regulatory requirements, helping you stay compliant and avoid penalties.
7. Enhanced Collaboration and Reporting
Collaborative Platform: Hopex's collaborative features foster collaboration across departments. The platform lets stakeholders easily share insights, updates, and feedback.
Reporting and Dashboards: Generate comprehensive reports and dashboards that provide real-time insights into your business architecture. These tools help you track progress, make informed decisions, and communicate with stakeholders.
8. Continuous Improvement
Performance Monitoring: Use Hopex to continuously monitor and evaluate the performance of business processes and capabilities. This ongoing assessment helps identify areas for improvement and ensures sustained operational excellence.
Feedback Loops: Establish feedback loops to incorporate lessons learned and adjust strategies. Hopex supports continuous improvement by enabling regular reviews and updates to your business architecture.
AI and Business Architecture Strategy
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing various aspects of business operations, and its integration with Business Architecture Strategy can provide significant advantages. Here's how AI can enhance your Business Architecture Strategy:
1. Enhanced Data Analysis and Insights
- Big Data Integration: AI can process vast amounts of data from various sources, providing valuable insights that inform business architecture decisions.
- Predictive Analytics: AI algorithms can predict future trends and behaviors based on historical data. This capability allows organizations to anticipate changes, optimize processes, and make proactive decisions.
2. Improved Decision-Making
- Data-Driven Decisions: AI provides data-driven insights that enhance decision-making processes.
- Scenario Planning: AI can simulate different scenarios and their potential impacts, helping business architects evaluate various strategies and choose the most effective ones.
4. Enhanced Capability Mapping and Management
- Dynamic Capability Mapping: AI can dynamically map business capabilities, continuously updating the architecture based on real-time data and changes in the business environment.
- Capability Gap Analysis: AI performs detailed gap analysis by comparing existing capabilities with desired future states. It identifies areas that need improvement and suggests targeted initiatives to bridge gaps.
5. Improved Customer Experience
- Personalization: AI enhances customer experience by providing personalized interactions and services. Business architecture strategies can incorporate AI-driven personalization to meet individual customer needs effectively.
- Customer Journey Analysis: AI analyzes customer journeys, providing insights into customer behavior and preferences.
6. Risk Management and Compliance
- Risk Identification and Mitigation: AI identifies potential risks by analyzing patterns and anomalies in data. It suggests mitigation strategies, helping organizations manage risks proactively.
- Regulatory Compliance: AI ensures compliance with regulations by continuously monitoring and analyzing compliance-related data. It alerts organizations to potential compliance issues, reducing the risk of penalties.
7. Strategic Alignment and Roadmap Development
- Aligning AI Initiatives with Business Goals: AI helps align AI initiatives with overall business goals, ensuring that AI investments support strategic objectives.
- Roadmap Development: AI assists in developing strategic roadmaps by providing data-driven insights and predictions. This leads to more accurate and achievable roadmaps that guide the organization toward its goals.
8. Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
- AI-Powered Collaboration Tools: AI enhances collaboration by providing tools facilitating communication and information sharing among stakeholders.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): AI-powered NLP tools improve communication by analyzing and interpreting human language.
9. Continuous Improvement and Innovation
- Continuous Monitoring and Feedback: AI continuously monitors business processes and provides real-time feedback. This ongoing assessment helps identify areas for improvement and ensure continuous optimization.
- Fostering Innovation: AI fosters innovation by identifying new opportunities and suggesting innovative solutions. It encourages a culture of continuous improvement and creativity.
Summary
As businesses face increasing pressure to be agile and responsive, the importance of business architecture will only grow. Organizations that invest in developing and maintaining a robust business architecture strategy will be better equipped to leverage opportunities, mitigate risks, and achieve sustained growth. In an era where change is the only constant, a well-defined Business Architecture Strategy is the key to thriving in the modern business world.
FAQs
Business architecture strategy is a discipline within enterprise architecture that focuses on defining an organization's structure and operation to achieve its business goals and objectives. It involves designing business capabilities, processes, and models that align with the overall corporate strategy and ensure alignment between business and technology.
Business architecture is essential as it provides a holistic view of an organization's business functions and operating model. It helps drive business initiatives, enabling the organization to effectively implement strategies and translate them into executable actions from strategy to execution.
The critical elements of business architecture include defining business capabilities, developing business capability maps, creating a business model canvas, and ensuring alignment between business processes and technology architecture.
Effective business architecture can help organizations enhance business value, improve business strategies, and provide a clear definition of how the business operates. It enables the organization to take a structured approach to evolving business needs and successfully implementing changes.
A business architect is responsible for designing and implementing architecture frameworks that align with the organization's business unit goals and objectives. They work towards developing architecture practices that support the organization in achieving its business objectives.
Enterprise Architecture Related Content
Shift from a documentation tool to an operational tool and accelerate business transformation
MEGA HOPEX for Enterprise Architecture
Request a demonstration of HOPEX for EA, and see how you can have immediate value of your projects.